The Model Builder is one of the novel features of AFFINImeter. Through the model builder AFFINImeter offers an unlimited amount of thermodynamic models for ITC data analysis. The overall binding equilibria within the species involved in the experiments is easily drawn by the user directly in chemical language. Then AFFINImeter translates the resulting reaction scheme into robust binding models to be used to isotherm ITC simulation or to perform Isothermal Titration Calorimetry curve fitting.
The model builder is a versatile tool, it allows to design models involving up to three different species (i.e. the case of two ligands that compete with each other to bind a macromolecule) and has the advantage to selectively place them in the syringe cell and/or in the calorimetric cell.
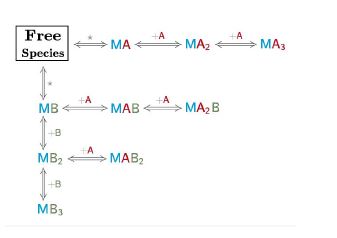
It also allows the design of models for dissociation, ranging from simple homodimers to higher-order oligomers. During the model construction no mathematical equations are required, once the whole set of binding interactions is defined by the user in the reaction builder, AFFINImeter internally generates the system of equations that define the reaction scheme proposed. The new model (reaction scheme and equations) is saved internally by AFFINImeter and listed in the user’s database so that can be utilized anytime so simulate or fit data.
AFFINImeter-ITC offers an exclusive unlimited amount of personalized model families including
- Unrestricted Competitive Sequential Binding with no limitation in the stoichiometry of the binding model.
- Competitive Multiple and Independent Sets of Identical and Independent Sites.
- Dissociation of any chemical species including homogeneous n-mers, heterogeneous complexes and even micelles.
With this extensive offer of model families the user will be able to perform the thermodynamic characterization of a vast variety of biological and physicochemical processes from ITC measurements. A few examples of classical and new applications of ITC experiments that you can analyze with AFFINImeter are:
- Protein-ligand or host-guest complex formation with unlimited stoichiometries
- Competition of different molecules to occupy a given binding site even for high order complexes
- Binding between ligands and polymers or large macromolecules with any number of (independent) sets and/or sites
- Dissociation/aggregation of supramolecular heterogeneous species including protein oligomers
- Structural and thermodynamic information of large aggregates, including micelles: aggregation number, enthalpy of formation, Gibbs energy and dilution heat of monomers and aggregates